
Plastic vs. glass coverlens
An overview
04.09.2023 // D. Casadei
There are basically two different types of cover lens material: glass and plastic. The decisive factor in deciding between the two materials is usually the desired hardness. Nowadays, glass cover lenses are mostly used due to various factors, which is why they are also called cover lenses.
What to expect:
In this blog article, we will discuss the different materials available on the market, show you what advantages or disadvantages they have, and discuss together which cover lens is the best solution for your display and application.
Glass Materials
Structure
- Glass is an inorganic solid that is usually transparent, hard and brittle.
- There are several methods for making glass, but the most common involves heating the base materials to form a molten liquid and then cooling it rapidly so that the atoms of the liquid have a random arrangement.
- Depending on the desired properties, various raw materials, also called fluxes, can be added to the base materials.
- After melting, the glass is referred to as a glass substrate. Depending on the application, the glass substrate can be strengthened by thermal or chemical hardening, but more on this later. A cover glass can be made from different types of glass substrates, which have different thicknesses and material properties. We would now like to discuss the two most common material groups of cover glasses below.
Soda-lime glass
- Soda-lime glass is the most commonly produced type of glass.
- Composition: The glass is composed of 70% silicon oxide (SiO), 15% sodium oxide (NaO), and 9% calcium oxide (CaO), with traces of other compounds. The soda ash is a melting agent that lowers the melting temperature of the silica, while the lime serves as a stabilizer for the silica. This glass is:
- Chemically stable: Soda-lime glass is composed of atoms that have very strong atomic bonds. Strong bonding forces hold the atoms tightly together, making it difficult for other substances to erode the glass and affect its structure.
- Hard: Soda-lime glass has a Mohs hardness scale of 6 to 7, indicating high abrasion resistance. Soda-lime glass can be hardened by heat or a suitable chemical.
- An electrical insulator: Because of its high resistivity and low dielectric constant, soda lime glass conducts electricity very poorly. Soda-lime glass is therefore suitable for insulating electrical products.
Aluminum silicate glass
- This glass has characteristic resistance to high temperatures and chemical influences.
- Composition: Aluminosilicate is a mineral-based material containing 57 - 60% silicon dioxide (SiO2) and 16 - 20% aluminum oxide (Al2O3), as well as a small amount of about 5 - 7% calcium oxide (CaO), 6 - 12% magnesium oxide (MgO), boron trioxide (B2O3) and other cations. This glass is particularly resistant to:
- Scratches and high tensile strength: Aluminosilicate glass is popular for manufacturing mobile devices because it is scratch resistant, which is very common in mobile devices. The high alkali content in aluminosilicate glass makes this possible.
- High temperatures: The annealing temperature of aluminosilicate glass reaches up to 800°C, which gives the glass material high heat resistance compared to other similar glasses. It has a similar melting temperature to ceramics.
- Chemical degradation: Aluminosilicate has very high chemical resistance due to a low dissolution rate of only 10-4 g/(m2-day).
Glass Hardening Process
Heat tempered glass
- The glass is heated at a high temperature (varies depending on the glass substrate) to form a liquid.
- As the glass liquefies, the molecules realign in a more stable pattern.
- Once the molecules have had sufficient time to realign at the melting point, the glass is cooled at an accelerated rate. This process results in higher compression of the surface and edges, and the glass achieves a surface strength of at least 10,000psi (pounds per square inch).
- This process makes heat-tempered glass four to five times stronger than normal, untreated glass.
- Heat-tempered glass cannot be cut after processing and treatment. Heat tempered glass shatters or cracks into many and less dangerous small pieces. It is therefore usually referred to as safety glass. Because of its safety properties, it is used for industrial or automotive applications.
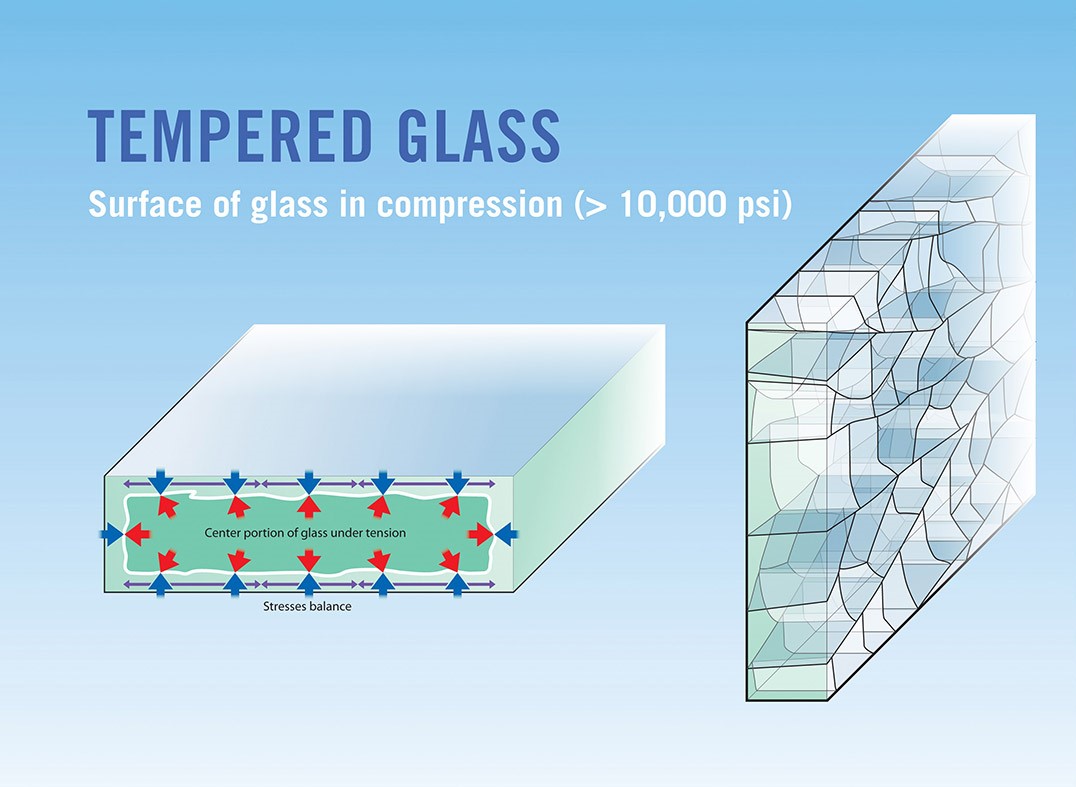
Heat treated glass
- In heat-treated glass, the cooling process is slower than that of heat-tempered glass.
- As a result, there is less compression of surfaces and edges and the glass achieves a lower surface strength of 3,500 - 7,000psi.
- Ultimately, heat-treated glass is about twice as strong as untreated glass. Heat treated glass breaks into large and sharp shards. Therefore, it is not considered safety glass by most industry standards.
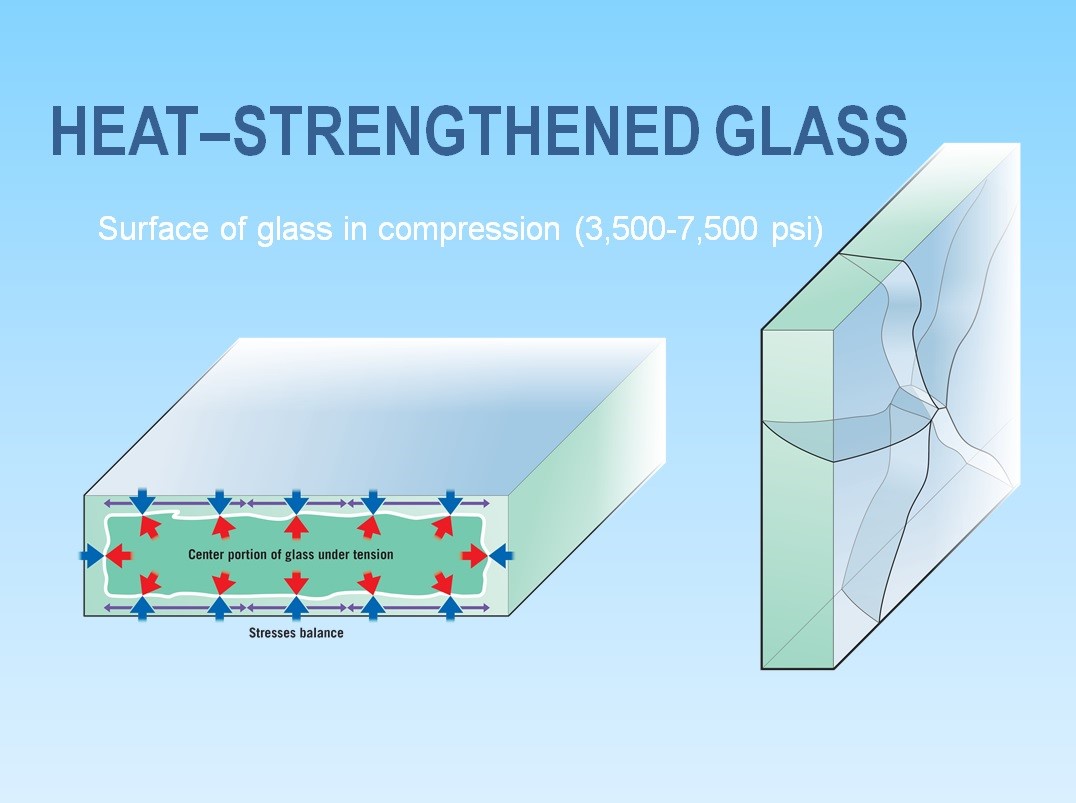
Chemically Tempered Glass
Chemically tempered glass is strengthened by the process of chemical bonding. The glass is immersed in chemicals at high heat, which allows ions to bond with the voids in the glass. The chemical process adds potassium bonds to the glass during this chemical reaction instead of the original sodium bonds.
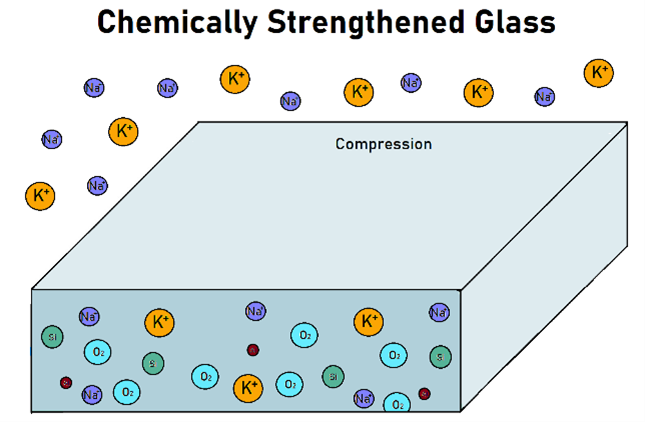
Chemically tempered glass has the advantage of maintaining optical clarity during the tempering process, and it is as strong as heat tempered glass. It also differs from heat-treated glass, where slight distortion of the glass surface may occur. Chemically treated glass can be cut or drilled after treatment, while this is not possible with heat treated and heat tempered glass.
Known glass brands
- Soda-lime glass is the most widely produced in the world and by various manufacturers. It is chemically treated and is a good option for LCDs that do not require additional protection of the glass. A standard soda-lime glass for an LCD has a hardness of about 5Mohs. This type of glass is not fragile and has normal durability, but it is not classified as extra strong display glass.
- Gorilla glass 3 from Corning (USA) is chemically tempered aluminum silicate glass made by ion exchange. The glass is immersed in molten potassium salt at 400°C. Through this process, the potassium displaces the sodium atoms from the compound. This glass has high surface strength and is resistant to cracks and scratches. The hardness grade is 7Mohs.
- Dragontrail-Glass from Asahi Glass (Japan) is similar to Gorilla Glass in that it is strengthened by chemical hardening. The hardness level of Dragontrail glass is 7Mohs, which is equivalent to Gorilla glass. With this hardness level, the glass is also scratch resistant. The glass can be very durable even with the minimum thickness.
All glasses can be obtained in the standardized thicknesses of 0.5mm, 0.7mm and 1.1mm as mother glasses in the market. Depending on the requirement, for example for a desired IK level, the manufacturing process for a specifically requested thickness must be examined in more detail.
Plastic materials
Depending on the application, a glass cover lens may be undesirable. For example in applications with high safety requirements, where even in the worst case no splinters are allowed. However, it is important to note that plastics as a material for cover lenses are generally not suitable for large temperature fluctuations. This is because the materials of LCD, optical or air-gap bonding and cover lenses bonded as display modules expand differently when exposed to temperature.
In addition, plastics are less durable under UV radiation compared to glass. The same applies to the printing of the cover lens, since there is a limited choice of printing methods. Especially for larger display modules and for outdoor use, we therefore do not recommend a design with plastic coverlens.
PC / Polycarbonate
- Is known for its ability to operate over a wide temperature range (-137°C to +124°C).
- Due to its high ductility, polycarbonate optics are not easily machined. The resin is more expensive than acrylic. It is an engineering plastic with high transparency and the highest impact resistance of all plastics.
- It is as transparent as glass and has the second highest transparency after acrylic resin. Polycarbonate has low water absorption and low shrinkage during molding, which gives the material excellent dimensional stability.
PMMA / Acrylic
- One of the most commonly used optical plastics and commonly referred to as acrylic.
- It is characterized by its excellent transparency and weather resistance, good mechanical strength and high surface hardness.
- It is sometimes referred to as "organic glass" because it has an excellent surface gloss and can be freely colored.
- The material is often used for optical lenses because it transmits lighter than glass and has a low refractive index.
- In addition to its excellent strength and transparency, it has excellent weather resistance and will not be damaged outdoors.
- However, it also has disadvantages such as high water-absorption, a change in refractive index when water is absorbed, and low heat resistance.
Conclusion
In general, it can be said that nowadays a glass cover lens is used in all industries and in most cases. This is not only due to the advantages mentioned above, but also from a price point of view. Due to the economies of scale in the production of cover lenses, they are usually cheaper to obtain than a plastic cover lens. Another point is the design aspect, especially the feel of the material. For this reason, glass is the preferred material, especially for high-end products. Nevertheless, both materials have their right to exist on the market and can play out their advantages depending on the application.
As your partner, we will be happy to advise you in making the right decision for your project.
We look forward to hearing from you!

